The other important geometry variables for scanning phantoms are the view diameter, scan diameter, focal length, and center-detector length. These variables are input into CTSim in terms of ratios rather than absolute values.
Phantom Diameter
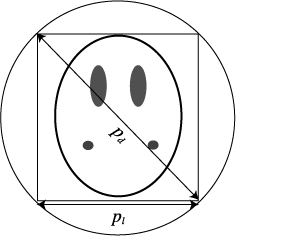
The phantom diameter is automatically calculated by CTSim from
the phantom definition. The maximum of the phantom length and
height is used to define the square that completely surrounds the
phantom. Let Pl be the width
and height of this square. The diameter of this boundary box,
Pd, is given by the
Pythagorean theorem and is

View Diameter
The view diameter is the area that is being processed
during scanning of phantoms as well as during rasterization of
phantoms. By default, the view diameter is set equal
to the phantom diameter. It may be useful, especially for
experimental reasons, to process an area larger (and maybe even
smaller) than the phantom. Thus, during rasterization or during
projections, CTSim will ask for a view ratio,
VR. The view
diameter is then calculated as
By using a VR less than 1, CTSim will allow for a view diameter less than phantom diameter. This will lead to significant artifacts. Physically, this would be impossible and is analogous to inserting an object into the CT scanner that is larger than the scanner itself!
Scan Diameter
By default, the entire view diameter is scanned. For
experimental purposes, it may be desirable to scan an area either
larger or smaller than the view diameter. Thus, the concept
of scan ratio, SR,
arises. The scan diameter,
Sd, is the diameter over
which x-rays are collected and is defined as
Focal Length
The focal length,
F,
is the distance of the X-ray source to the center of
the phantom. The focal length is set as a ratio,
FR,
of the view radius. Focal length is
calculated as
For parallel geometry scanning, the focal length doesn't matter. However, for divergent geometry scanning (equilinear and equiangular), the focal length ratio should be set at 2 or more to avoid artifacts. Moreover, a value of less than 1 is physically impossible and it analagous to having the x-ray source inside of the view diameter.
Center-Detector Length
The center-detector length,
C,
is the distance from the center of
the phantom to the center of the detector array. The center-detector length is set as a ratio,
CR,
of the view radius. The center-detector length is
calculated as
For parallel geometry scanning, the center-detector length doesn't matter. A value of less than 1 is physically impossible and it analagous to having the detector array inside of the view diameter.