For parallel geometry, the detector length is simply the scan diameter.
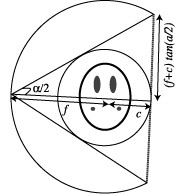
For divergent beam geometries, the size of the detector array also depends upon the focal length: increasing the focal length decreases the size of the detector array.
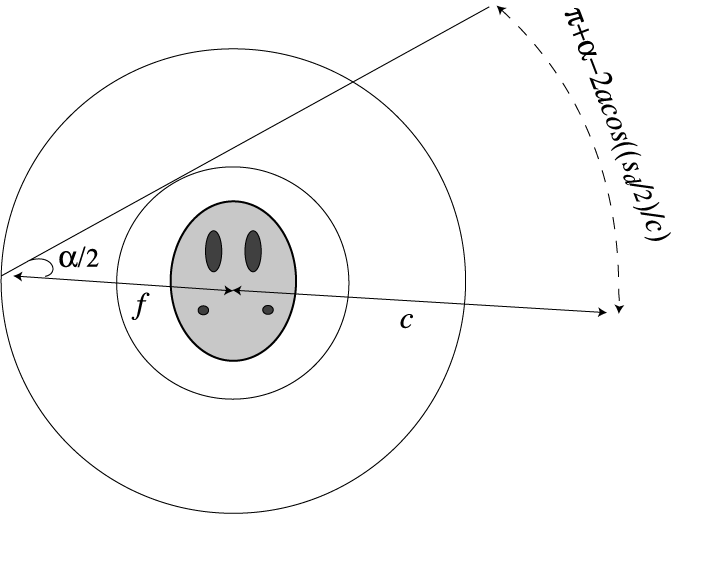
For equiangular geometry, the detectors are equally spaced around a arc
covering an angular distance of alpha as viewed from the source. When
viewed from the center of the scanning, the angular distance is
pi + alpha - 2 x acos ((Sd / 2) / C))
The dotted circle
indicates the positions of the detectors in this case.

For equilinear geometry, the detectors are equally spaced along a straight
line. The detector length depends upon
alpha and the focal
length. This length,
Dl, is calculated as